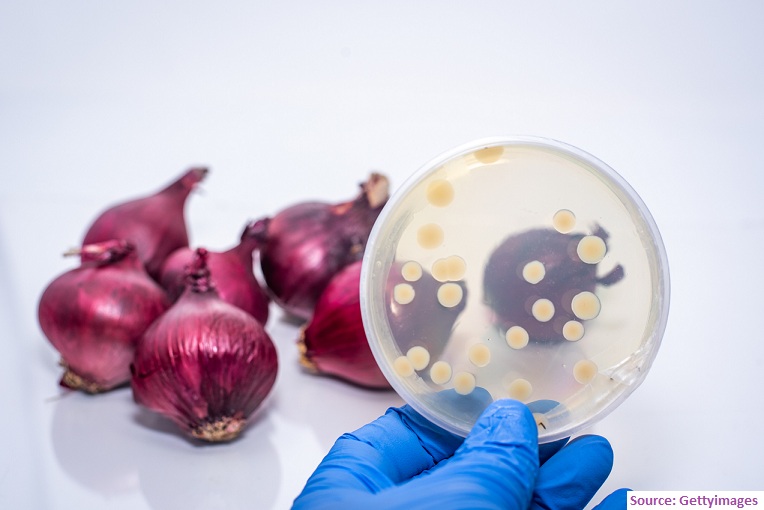
It is well known that antimicrobial resistance (AMR) leads to problematic infections, threatens the success of routine surgery and cancer treatments. As per WHO, AMR is estimated to kill 10 million people per year by 2050. In this regard, one of the troublesome areas is the incidence of biofilm-associated resistant infection. The cost of biofilm infections is estimated to be around over a billion pounds every year of the UK’s National Health Service which is expected to increase even more. This indeed surges the need for novel antimicrobials are urgently needed to combat drug-resistant bacteria and to overcome the inherent difficulties in treating biofilm-associated infections.
In the present times, we have somehow really forgotten the valuable role of plants and other natural materials which were the only remedies in the historical era. The current study in the UK has gone back and tried bridging the antibiotic discovery gap by exploiting the antimicrobial activity of natural products. The scientists reconstructed a 1,000-year-old remedy containing onion, garlic, wine, and bile salts, known as ‘Bald’s eyesalve’, and showed it had promising antibacterial activity. The bactericidal activity extends to a range of Gram-negative and Gram-positive wound pathogens in planktonic culture. Further, it was observed that the potent anti-biofilm activity of Bald’s eyesalve cannot be attributed to a single ingredient and requires the combination of all ingredients to achieve full activity. The current work highlights the need to explore not only single compounds but also mixtures of natural products for treating biofilm infections.
For more information, visit the website of Scientific reports (Link)