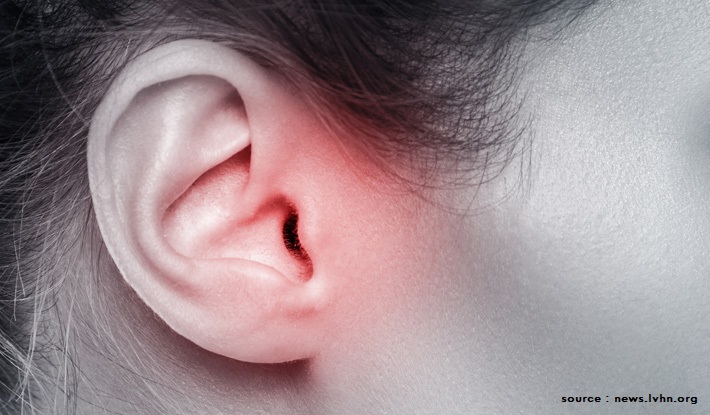
Inadequate dose of antibiotic treatment is one of the major factors contributing to antibiotic resistance. An outer ear infection is a common problem in various age groups. It is caused by mainly Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus. The antibiotic treatment against outer ear infection involves administration of the antibiotic drops, multiple times per day for 7-14 days. Such a treatment regimen is difficult for some people especially with hand or head tremors, swimmers, geriatric population, military people, and those who have limited access to healthcare facilities.
A study led by Dr. Monica Serban (University of Montana, United States) developed a novel delivery method to treat the outer ear infection. They used tetraethyl orthosilicate and polymers with high molecular weight to design the delivery method. The antibiotic-containing hydrogel is initially in the liquid form and stable through a wide range of temperatures. After applying into the ear it immediately forms a gel and ensures sustain release of antibiotics. The delivery system in the form of hydrogels maintains the efficacy of the antibiotic without any adverse effect.
Thus, the drug delivery system can be easily translated into a product and is effective in reducing the chances of antibiotic resistance.
To read more click on the LINK