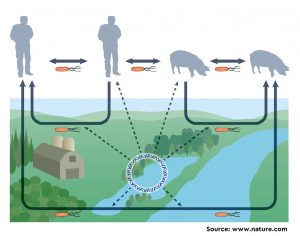
The rapid increase in Antibiotic resistance (ABR) is a global concern. In such a scenario, ABR incidences can be effectively regulated by limiting its spread through the implementation of good practices in all the sectors including plant farming.
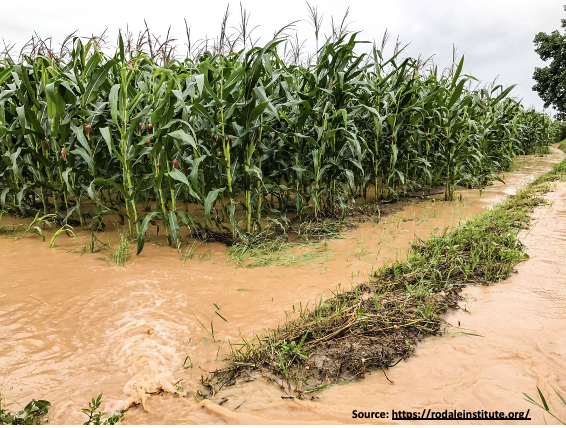
The livestock waste is generally considered as excellent manure for overall plant growth or crop yield. However, livestock wastes have become one of the hotspots of antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) and antibiotic-resistant bacteria (ARBs) due to the enormous use of antibiotics in animal farming as a prophylactic or treatment strategy. Humans, animals, and the environment are closely interlinked. Hence, there is a huge risk of the spread of antibiotic resistance genes from soil to humans through the water. In order to reduce water contamination, best management practices are followed. One such recommendation is a setback distance. It is a minimum distance required between the source of contaminant and water bodies. Few regulatory agencies have declared some setback distances for some contaminants. However, there are no such standards for antibiotics or ARGs.
A recent study led by Dr. Xu Li (University of Nebraska-Lincoln, United States) has determined the setback distance required to minimize the dissemination of antibiotics and ARGs from agricultural land to water bodies following the usage of swine manure slurry on the land. The researchers’ team specifically investigated the effect of several setback distances on the transport of antibiotics and ARGs from soil to water under normal conditions also after two consecutive rainfalls. The study estimated that a setback distance in the range of 34–67 m may limit manure-borne antibiotics and ARGs in agricultural runoff under the experimental conditions. As the study covered all the parameters to determine the setback distances it can be used as a model study to determine the setback distances required to protect the transport of the antibiotics and ARGs from manure to surface water at other geographical locations.
To read more: Follow the Link