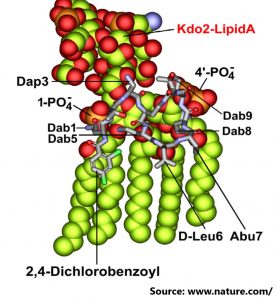
The most biodiverse habitat on earth is the soil. It contains billions of bacterial cells, bioactive compounds including antibiotics and antimicrobial resistance genes (ARG). These ARGs are transferred from soil to human through direct contact, food chain and as a transfer stop to water/air environment. In addition to this intrinsic resistome, sustained selection pressure on bacteria by antibiotic use, heavy metal and disinfectants has led to enrichment of ARG in soil. The major source for this enrichment is the waste water treatment plants. The other sources that contribute ARG into the soil are improper disposal of antibiotics, heavy metals and disinfectants from clinics, industries and households, animal manures and air pollution.
To read the entire article, visit the website of Environment International journal [link]