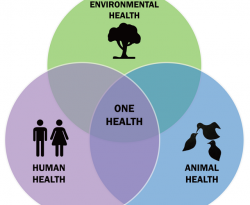
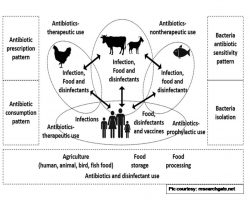
Antimicrobial use in food animals and human health: time to implement ‘One Health’ approach
It is well known now that the non-prudent use of antimicrobials in animals has contributed drastically to the development of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) in humans. For instance, the statistics from the United States and Europe indicate that around 70% of antimicrobials are sold for use in food animals. However, the…