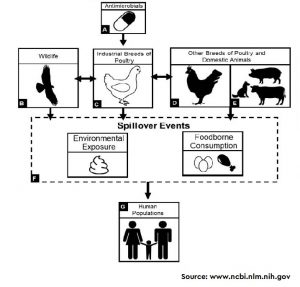
Global antibiotic consumption has been increased a lot in the last few years. It is widely known that antibiotic therapy affects the human gut microbiome. Moreover, dysbiosis of the gut microbiome has been recently linked to several intestinal and extra-intestinal diseases.
A recent study by a team of UK researchers established the link between antibiotic consumption and colorectal cancer. They are pioneers in investigating the association of antibiotic consumption with colorectal cancer. The study was carried out using Scottish primary care data. Patients diagnosed with colorectal cancer between years 1999 to 2011, were considered for the study. Exposure of these patients to antibiotics was determined and they were categorized into 1, 1-15, 16-60 and >60 days. The result showed that the use of antibiotics was linked to an increased risk of colon cancer in both age groups (below and above 50 years). It was also found that antibiotic usage increases the risk of proximal colon cancer especially in people under 50s.
Thus, judicious use of antibiotics is not only essential to avoid antibiotic resistance but also important to avoid other diseases such as colorectal cancer.
To read more on the topic, kindly visit the website of Annals of Oncology (Link).