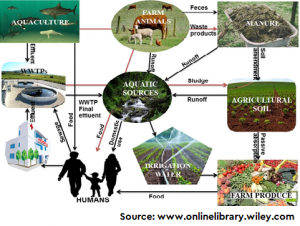
The issue of misuse of antimicrobials is increasing day by day in both humans and animal sector. This exposure of antibiotic/antimicrobial residues to the human, animals, plants and thus environment can further worsen the situation. Further, the problem of increasing resistance will not allow the treatment of patients, success of surgeries, organ transplants, etc. The World Health Organization has already come up with a global action plan against antimicrobial resistance. It emphasises on the prudent use of antimicrobials, good infection prevention and control practices, awareness among people, better technology advancement for the diagnostic and treatment opportunities. However, still all these factors are contributing to increase the incidence of antimicrobial resistant infections. A recent review article by Rahman et al. (2022) highlights and discusses in details the overall journey of antimicrobial resistance to better understand the phenomenon and then find out the impact of antimicrobial stewardship in combating the same.
The review discusses the journey from beginning talking about the history of development of antibiotics, followed by how the resistance started developing. Further, it discusses how microbial resistome can be studied and their antibiotic resistance can be determined. The detailed profile of the genes involved in providing resistance to different microbes is discussed along with molecular mechanisms. The relationship between the use and misuse of antibiotics in human and animal healthcare is explained. The current approaches followed to develop newer antibiotics are mentioned precisely. While in the last section, the impact of different factors affecting the antibiotic resistance – viz. poor knowledge, lack of awareness, lack of laws and policies are mentioned. In the end, the role of global action plan to curb the impact of antibiotic resistance is highlighted with a greater emphasis on antimicrobial stewardship program. Thus, the authors pointed that a single approach cannot be a solution to this global health issue and multisectoral One Health approach is the key involving coordination among lawmakers, animal healthcare staff, pharmaceutical industries, regulatory agencies, and medication distributors.
To know more, please visit the website of journal Antibiotics (Link)