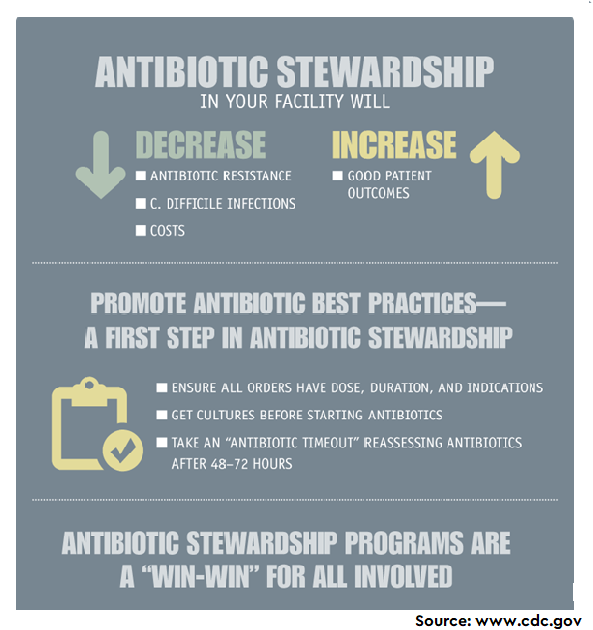
Antibiotic stewardship (AS) is the effort to measure antibiotic misuse. The AS intent to improve antibiotic prescribing by clinicians and use by patients so that antibiotics are only prescribed and used when needed; to minimize misdiagnoses or delayed diagnoses leading to underuse of antibiotics; and to ensure that the right drug, dose, and duration are selected when an antibiotic is needed (CDC).
Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania (United States), surveyed 4th-year students of undergraduate medical education (UME), which showed that only one-third of respondents reported feeling comfortable with the principles of antimicrobial prescribing, and 90% of them expressed the desire for additional instruction. Learning the importance of AS, the authors gave an immersive curriculum focused on teaching AS concepts at the UME level.
The course ASSURE included teaching materials as well as learning activities aimed to immerse students in many aspects of AS. The study also includes enhancing practical knowledge through active engagement in AS activities. Only a handful of them felt confident with matters including antibiotic selection (19%), dose for agents requiring therapeutic drug monitoring (6%), and adverse effects before the course. Confidence levels increased for all students and in all domains once the training was completed. This course’s objectives and structure could serve as an example to guide the development of similar curricula at some other institutions. For more details, visit the website of Oxford Academic (link).